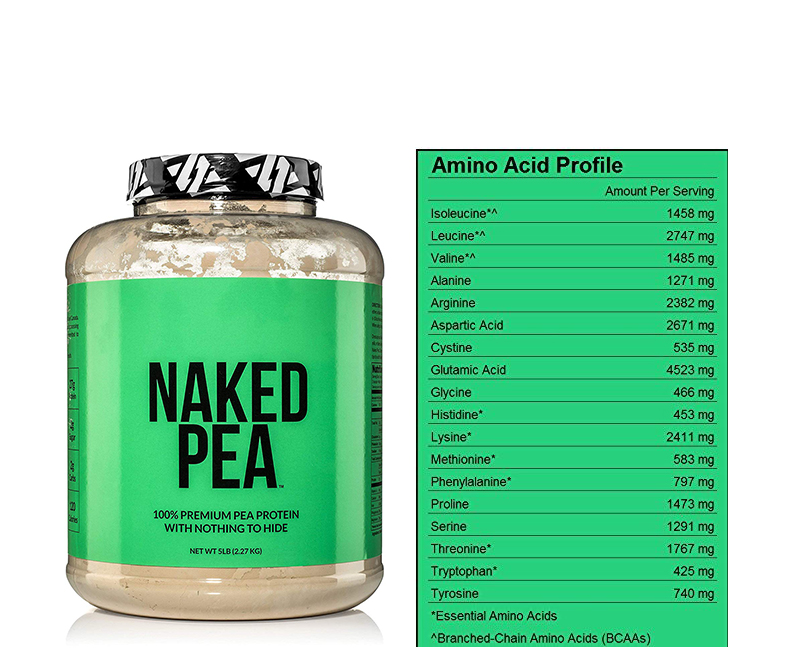
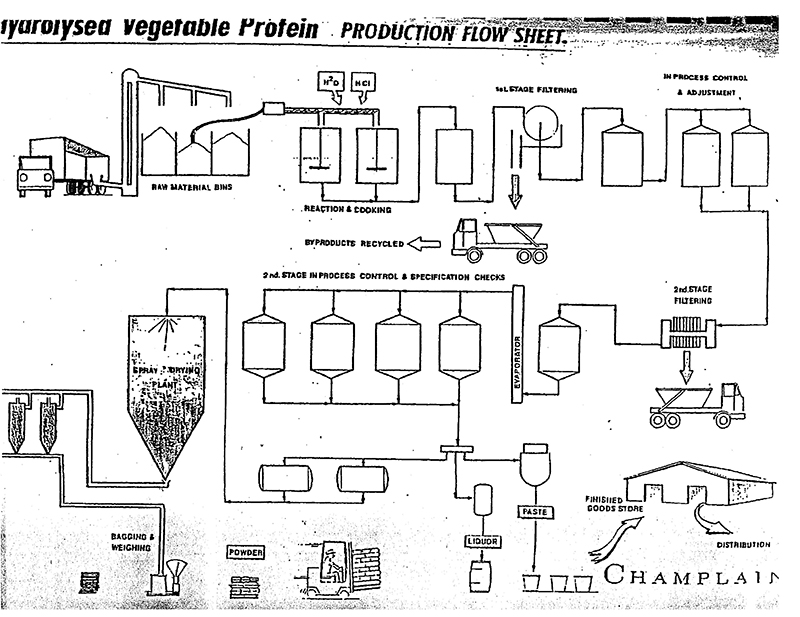
It has always been my opinion that the concept of umami was developed to promote the sale of monosodium glutamate, with a very large enterprise developed to promote the fiction.
When I was first introduced to “umami” I had a creeping suspicion that the concept of umami had been promoted in an effort to legitimize the use of monosodium glutamate in food, drawing attention away from the fact that monosodium glutamate is a neurotoxic amino acid which kills brain cells, is an endocrine disruptor (causing obesity and reproductive disorders), and is the trigger for reactions such as asthma, migraine headache, seizures, depression, irritable bowel, hives, and heart irregularities.
It’s common knowledge that there are glutamate receptors in the mouth and on the tongue. Could researchers be hired to produce studies demonstrating that glutamate containing food can stimulate those glutamate receptors, and then declare to the world that a fifth taste has been discovered — calling it umami? I wondered.
Never mind that for years monosodium glutamate was described as a tasteless white crystalline powder. Never mind that Julia Child, who in her later years was recruited to praise the use of monosodium glutamate, never once mentioned the additive in her cookbooks. Never mind that if there was taste associated with monosodium glutamate, people who are sensitive to MSG would be highly motivated to identify that taste and thereby avoid ingesting MSG – which they claim they cannot do.
It certainly would be wonderful, I thought, if the glutamic acid in processed free glutamic acid (MSG) had a delicious, robust, easily identifiable taste of its own. Even if the taste was unpleasant instead of delicious, it would still be wonderful — at least the adults who are sensitive to MSG could identify the additive in their food and avoid eating it. MSG-induced migraine headaches, tachycardia, skin rash, irritable bowels, seizures, depression, and all of the other MSG-induced maladies, could become nothing more than bad memories.
Sometime after Olney and others demonstrated that monosodium glutamate was an excitotoxin — killing brain cells and disrupting the endocrine system — Ajinomoto, Co., Inc. began to claim that their researchers had identified/isolated a “fifth taste.” The “fifth taste,” they said, was the taste of processed free glutamic acid. This alleged fifth taste was branded “umami.”
The word “umami” has been in the Japanese vocabulary for over a century, being in use during the Edo period of Japanese history which ended in 1868. In the 1990s, it was written that “umami” can denote a really good taste of something – a taste or flavor that exemplifies the flavor of that something. It was said that the taste of monosodium glutamate by itself does not in any sense represent deliciousness. Instead, it is often described as unpleasant, and as bitter, salty, or soapy. However, when monosodium glutamate is added in low concentrations to appropriate foods, the flavor, the pleasantness, and the acceptability of the food increases.
For years, certainly up to the turn of this century, monosodium glutamate had been thought of as a flavor enhancer – like salt. Something that enhances the taste of the food to which it is added. Early encyclopedia definitions of monosodium glutamate stated that monosodium glutamate was an essentially tasteless substance. The idea (advanced by Ajinomoto) that monosodium glutamate has a taste of its own, as opposed to being a flavor enhancer, is relatively recent. Not just a taste of its own, mind you, but something newsworthy that could attract national or international attention. A fifth classification of taste added to the recognized tastes of sweet, salty, bitter, and sour.
The idea that monosodium glutamate has a unique taste can be tracked in the scientific literature if you read vigilantly. I don’t know whose brainchild it was, but it certainly was a brilliant move on the road to marketing monosodium glutamate – a move precipitated by a growing public recognition that monosodium glutamate causes serious adverse reactions. And even one step farther up the brilliance chart, this monosodium-glutamate-taste-of-its-own was given a name. Naming things makes them easy to talk about and gives them respectability. The monosodium-glutamate-taste-of-its-own was named “umami.”
We started writing about umami years ago. We were already familiar with the research that the glutamate industry used to claim that umami was a fifth taste, and we knew that, with possible rare exception, all of that research had been funded by Ajinomoto and/or their friends and agents. We also sensed that researchers outside of the direct employ, or outside of the indirect largess of the glutamate industry, found the idea of a fifth taste to be without merit.
We thought that we should begin by making the case that what was called the “taste” produced by monosodium glutamate is not a taste, per se, but is little or nothing more than the vague sensation that nerves are firing. We would start by reminding our readers that what industry calls the “taste” of monosodium glutamate is its manufactured free glutamic acid; that glutamic acid is a neurotransmitter; and that as a neurotransmitter, glutamic acid would carry nerve impulses to nerve cells called glutamate receptors, and trigger responses/reactions. Then we would explain that there are glutamate receptor cells in the mouth and on the tongue, and that monosodium glutamate could trigger reactions in those glutamate receptors — leaving the person who was ingesting the monosodium glutamate with the perception that food being ingested with it had a bigger, longer lasting taste than it would have had if there was no monosodium glutamate present.
Ask Ajinomoto, and they will tell you that there are studies that prove that umami is a fifth taste. Review of those studies has proved to be extremely interesting, but when read carefully, offers no proof that monosodium glutamate does anything more than stimulate receptors in the mouth and on the tongue and promote the perception of more taste than the ingested food would otherwise provide.
I actually spoke with one of the umami researchers on the phone, a Dr. Michael O’Mahoney, Professor in the Department of Food Science and Technology, UC Davis. He was doing research for the glutamate industry and, therefore, could certainly provide information.
Dr. O’Mahoney was warm and friendly, but said that because he had a contract with Ajinomoto to study the taste of monosodium glutamate he was not able to share information with me. An academician who refused to share information was an animal I had not met before.
Based on personal observations and conversations with MSG-sensitive friends, I have become increasingly certain that monosodium glutamate has no taste; that in stimulating the glutamate receptors in the mouth and on the tongue, glutamate causes the person ingesting monosodium glutamate to perceive more taste in food than the food would otherwise have; that umami is a clever contrivance/device/public relations effort to draw attention away from the fact that processed free glutamic acid and the monosodium glutamate that contains it are toxic.
And taste? A savory taste? Given what I know about Ajinomoto’s rigging studies of the safety of monosodium glutamate, I couldn’t help but wonder if they might have done something unsavory to support their claim that monosodium glutamate has a savory taste.
- They certainly have studies allegedly demonstrating that monosodium glutamate has a savory taste. Were those studies rigged?
- Did Ajinomoto feed something to the genetically modified bacteria that excrete their glutamic acid that would cause the glutamic acid to have a taste? A savory taste?
- When the L-glutamic acid used in monosodium glutamate is produced, there are unavoidable by-products of production. Does one of those by-products contribute a savory taste?
- Is some savory flavoring added to the monosodium glutamate product before it leaves the Eddyville plant?
- Is “savory taste” a fiction invented by Ajinomoto and reinforced through repetition of the concept?
When it comes down to what really matters, whether there are four or five tastes is irrelevant.
When it comes down to what really matters, whether monosodium glutamate is a flavor enhancer or a flavor itself is inconsequential.
What really matters is that chemical poisons are being poured into infant formula, enteral (invalid) care products, dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals and processed foods — and one of those chemical poisons is manufactured free glutamic acid, found in monosodium glutamate and four dozen or so other ingredients with names that give no clue to its presence. That’s my opinion.
Adrienne Samuels, Ph.D.
Director, The Truth in Labeling Campaign