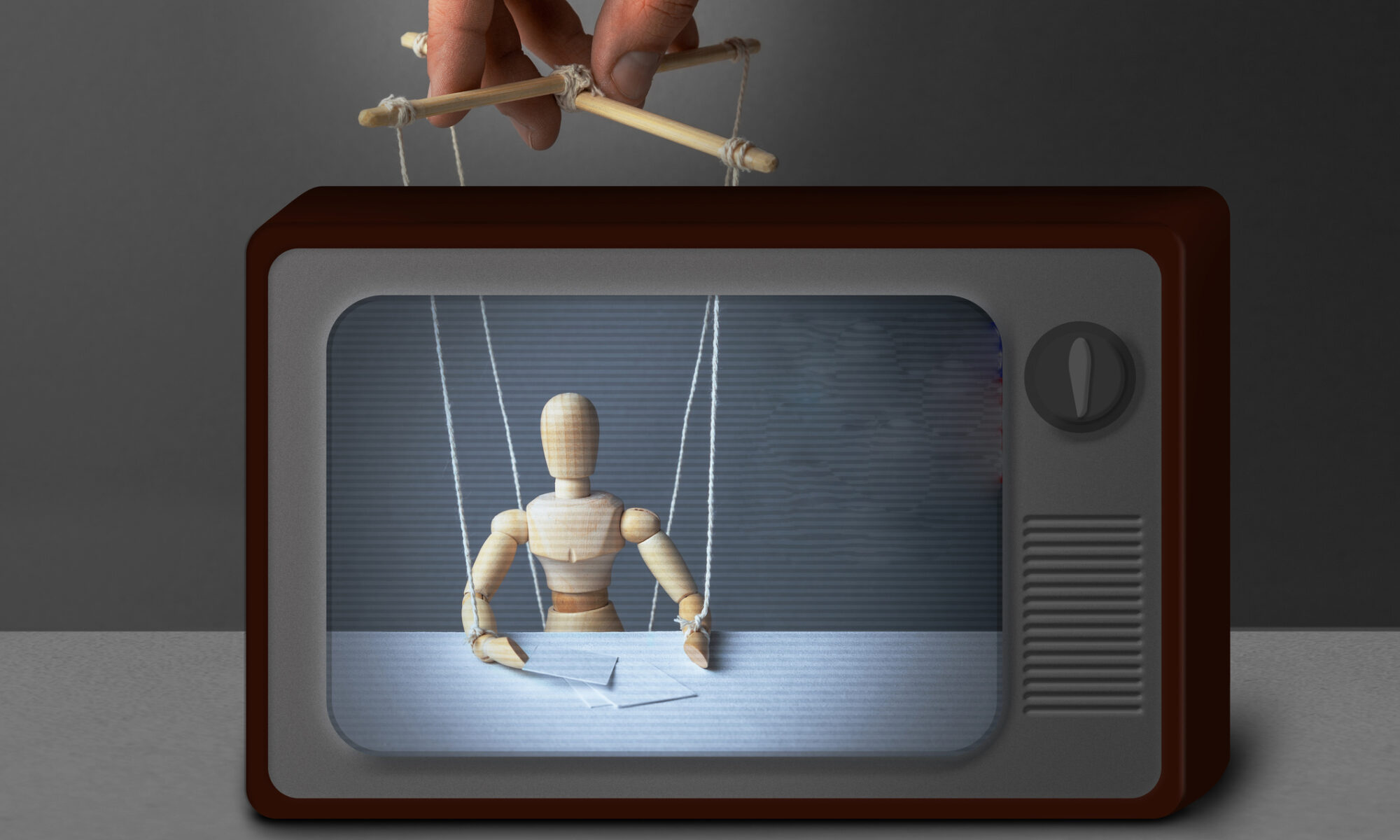
If you have enough money and the right contacts, you too can make up your own ‘news’
Ajinomoto, the world’s largest manufacturer of monosodium glutamate (MSG), and its PR firm, Edelman Public Relations, have recently joined with CBS to recycle the Glues favorite propaganda pieces disguised as news.
Aired recently on both CBS Mornings and the network’s highly regarded Sunday Morning show led by veteran journalist Jane Pauley, as well as a Bay area affiliate station, the productions are straight out of the Edelman/Ajinomoto playbook.
The often-repeated blueprint goes like this:”
- Use a headline that shows there’s controversy, but not to worry because you can trust that this article/video will give you the real facts:
Yes, MSG has a bad reputation but it’s now making a “comeback.”
“Science” has proven that there’s nothing to worry about!
Things need to be “set straight.”
2. Repeat the well-worn fiction that a 55-year-old letter is responsible for consumers considering that MSG might be toxic. Capitalize on its unique name “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome.” Ignore the multitude of studies clearly demonstrating that MSG causes brain damage.
3. Trot out the “Expert,” who talks about “The Letter” and alludes to how it’s been refuted by “decades of research,” without the expert actually citing any.
4. Bring on the “Chefs,” who will be shown cooking up a storm of delicious food sprinkled with MSG and give some to the reporter to taste. “Yum!”
5. Introduce the xenophobic zinger. This is indeed the perfect example of the diabolical genius of the folks at Edelman PR, filling the airwaves with the concept that avoidance of MSG isn’t based on science, but is actually nothing more than anti-Asian hate speech in disguise.
“Ajinomoto established that deep-rooted xenophobia is at the center of MSG’s complicated history in the U.S.” Edelman stated in a 2019 press release. That seemingly crazy concept has caught on so well that even a book I co-authored about food additives was targeted by a “reader review” that claimed it’s “not cool to promote myths rooted in racism.”
The Edelman team works long and hard at selling the product they’ve been paid to sell. And they have the media connections to make it happen. But despite the constant use of such expensive and wide-spread propaganda, recognition that MSG is harmful continues to be acknowledged by consumers. It looks like growing numbers of consumers are realizing that they are getting sick following meals that include MSG or some other ingredient that contains its processed free glutamate, and that the more consumers know the harder Ajinomoto and Edelman will work to sell us its disinformation. Remember that currently the only consumer group to reveal what’s going on with MSG is the Truth in Labeling Campaign.
Interesting thing about CBS, the network also makes itself available to spin news on behalf of Big Pharma. A January 60 Minutes program was identified as “an unlawful weight loss drug ad” for the med Wegovy by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. “The 60 Minutes program looked like a news story, but it was effectively a drug ad,” the group Committee said in a press release. PCRM also stated that Novo Nordisk, which makes Wegovy, paid over $100,000 to the doctors CBS interviewed for the segment.
The blog links below (click on the headlines) will give you an idea of how extensive glutamate marketing is, and should leave you wondering whenever you read an article or watch a program: is it news or is it propaganda?
Linda Bonvie